Understanding Breast Cysts
A breast cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the breast tissue. You can have one or more cysts at a time. They can occur in one or both breasts. Breast cysts can be soft or firm and vary in size. In most cases, they aren't cancer (benign).
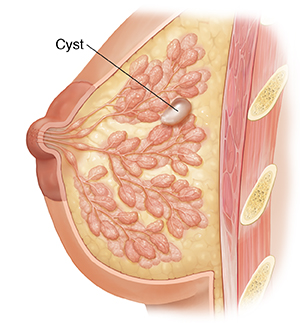
What causes a breast cyst?
Experts don’t know what causes breast cysts. They think that cysts form because of hormone changes that happen during a woman’s menstrual cycle. They can develop at any age, but are most common in women ages 35 to 50.
Symptoms of a breast cyst
Often, a breast cyst has no symptoms. The cyst may have been found during a breast exam or imaging test. If symptoms do occur, they can include:
-
A round or oval lump in the breast that can be seen or felt.
-
Pain, discomfort, or soreness around the lump.
-
A lump that grows larger or that feels more painful and sore just before your period.
Treatment for a breast cyst
Most breast cysts don't need treatment. They may even go away on their own. Breast cysts that are painful, large, or look abnormal by imaging may need to be treated. Options include:
-
Drainage (aspiration) of the cyst. The health care provider uses a needle and syringe to remove the fluid from the cyst. In some cases, they may use ultrasound during the procedure to help see the cyst and guide the needle.
-
Surgery to remove the cyst. Your provider cuts the cyst out. It may need to be drained first.
Possible complications of a breast cyst
A breast cyst may go away but then form again. This can happen even after treatment. Also, additional cysts may form in the same or the opposite breast.
When to call your health care provider
Call your health care provider right away if you have:
-
A fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider.
-
Pain or soreness in the breast that doesn’t go away or that gets worse.
-
An abnormal lump in the breast.
-
A change in skin color over the breast.
-
Dimpling or puckering of the skin over your breast.
-
A nipple that becomes pulled in (retracted).
-
Dark or bloody discharge from your nipple.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
Online Medical Reviewer:
Marianne Fraser MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rajadurai Samnishanth Researcher
Date Last Reviewed:
1/1/2025
© 2000-2026 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.