A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Click a letter to see a list of medical procedures beginning with that letter.
Click 'Back to Intro' to return to the beginning of this section.
What is Gout?
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by too much uric acid buildup in your body. Gout often causes sudden pain and swelling in 1 joint, often the big toe or other joints in the feet. If not treated, it can lead to painful foot and joint deformities. It may lead to kidney problems. But by treating gout early, you can ease pain and help prevent future problems. Gout can often be treated with medicine and a change in diet. In severe cases, surgery may be needed.
What causes gout?
Gout is caused by too much uric acid in the body. This is a waste product made by the body. Uric acid is filtered out by the kidneys. If the uric acid level in your blood rises too high, it may form crystals. If these crystals are not treated and are kept in the body for a long time, they will cause severe health issues. These collect in the joints. This brings on a gout attack. A gout attack is inflammation in the joints that can cause sudden pain and swelling. If you have many gout attacks, crystals may form large deposits called tophi. Tophi can damage joints and cause deformity.
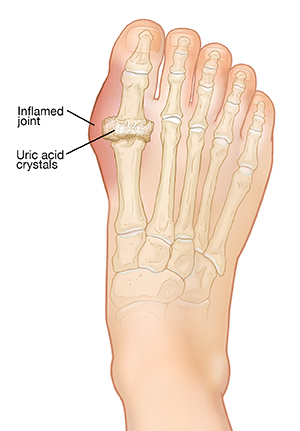
Who's at risk for gout?
People assigned male at birth are more likely to have gout. People assigned female at birth may have gout, but more often after menopause. Some health problems make gout more likely. These include obesity and high cholesterol. And some medicines can trigger a gout attack. These include water pills (diuretics). People who drink a lot of alcohol are at high risk for gout. Some foods can trigger a gout attack.
Things that may trigger a gout attack
-
Alcohol, especially beer, but also red wine and spirits
-
Some meats such as red meat, processed meat, turkey
-
Organ meats such as kidney, liver, sweetbread
-
Shellfish such as lobster, crab, shrimp, scallops, mussels
-
Some fish such as anchovies, sardines, herring, mackerel
Treatment
-
Make lifestyle changes. These include weight loss, exercise, reducing or eliminating alcohol intake, especially beer, and quitting tobacco use. Adding low-fat dairy foods may lower uric acid levels.
-
Limit certain foods and drinks. Reduce your intake of the foods and drinks listed above that may trigger a gout attack. Don't eat or drink things with high-fructose corn syrup. This is found in many foods. It's in some sodas and energy drinks.
-
Ask about your medicines. Some medicines may contribute to gout. This includes diuretics. Talk to your healthcare provider about other options.
-
Try medicines to reduce the amount of uric acid in the blood. These include allopurinol, probenecid, febuxostat, and lesinurad.
-
Take medicines to treat sudden gout attacks. These include NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), steroids, and colchicine.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Marianne Fraser MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rajadurai Samnishanth
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rita Sather RN
Date Last Reviewed:
3/1/2024
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.