A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
Caring for a Hearing Aid
The audiologist or hearing aid specialist will show you how to use your aid correctly and how to care for it. This may take several visits during the trial period. Stay in touch with your provider, and discuss any problems. Ask your audiologist where you can buy a battery tester, a drying container, and a forced air blower.
Daily cleaning
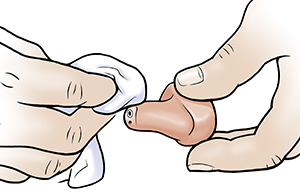
-
Follow the instructions for regular cleaning provided by the hearing aid manufacturer.
-
Wipe the aid with a soft, dry cloth or tissue.
-
Never put the hearing aid in water or use any cleaning solvents.
-
You may remove ear molds from the hearing aids and clean them with a mild soap solution. Use a forced air blower, not a hair dryer, to dry them. Make sure they are completely dry before you reattach them to the hearing aid.
-
Use a hearing aid drying container to keep moisture out of hearing aids and lengthen their life.
-
Ask your audiologist where you can buy a drying container and a forced air blower.
Controlling earwax
-
Earwax can plug your hearing aid and interfere with sound transmission. Wax inside the aid can cause the electronic parts to fail and may require expensive repair.
-
Your hearing aid specialist will show you how to clean the wax out. They can suggest several types of wax guards that prevent buildup.
-
If you have excessive wax production, you may need to have your health care provider remove the wax from your ear at least once a year.
Changing batteries
-
Your audiologist or hearing aid specialist will show you how to change the batteries correctly. Don’t force the tiny batteries in.
-
Batteries last from 5 days to a few weeks, depending on their size and use. Use a battery tester to make sure your batteries are at full strength. Ask your audiologist where to buy a battery tester.
-
Keep a small supply of fresh batteries on hand. Some types of hearing aid batteries fail suddenly. Others run down slowly.
-
Learn how to get rid of used batteries correctly. Keep them out of the reach of children and pets.
Emergency: When a child or pet swallows a battery
If your child swallows a battery:
-
Call the National Battery Ingestion Hotline right away at 800-498-8666.
-
Don't have your child throw up, and don't wait for symptoms.
-
Your child will likely need to go to the emergency room.
-
Don't let your child eat or drink anything until an X-ray is taken. An X-ray will often be needed right away to see if the battery has passed through the food tube (esophagus) into the stomach. If batteries are stuck in the esophagus, nose, or ear, they must be removed right away to prevent lasting damage.
-
If possible, bring the battery packaging with you. This will help health care providers figure out how much risk your child faces.
If your pet swallows a battery:
-
Take the animal to your veterinarian or emergency veterinary hospital right away.
-
Don't try to make your pet vomit.
-
If possible, bring the battery packaging with you. This can help the veterinarian figure out how much risk your pet faces.
Keep these emergency numbers posted:
When to call 911
Call 911 if the battery gets stuck in the child's throat and your child has any of the following symptoms:
-
Unable to talk
-
Loss of consciousness
-
Drooling from the mouth or unable to swallow their saliva
-
Trouble breathing
-
Wheezing
-
Blue, purple, or gray skin color
-
Sudden, severe pain
Special safety steps
Your hearing aid is a delicate piece of equipment. Handle it with care.
-
Don't expose your hearing aid to water while bathing or swimming. Don't expose it to extreme heat or cold.
-
Protect your hearing aid from small children who may break or swallow it.
-
Don't leave your hearing aid where it can be found by pets. Dogs find the high-pitched sound attractive and can quickly destroy an aid. If swallowed, batteries can also be deadly for pets.
-
Ask your hearing aid specialist about insurance to cover any damage or loss
Hearing aid batteries can cause devastating injuries if swallowed.
-
Keep the batteries in a secure place that is out of the reach of children.
-
Don't change batteries in front of children.
-
Don't store batteries near pills or in pill bottles. Don't leave batteries on bedside tables. People have swallowed batteries by mistake because they thought they were medicines. Look at every medicine before you take a pill.
-
Make sure all hearing aids for children have child-resistant battery compartments. Be sure the lock is on when the child is wearing the aid.
-
Ask your hearing aid specialist about battery recycling services in your area.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Ashutosh Kacker MD
Online Medical Reviewer:
Marianne Fraser MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Melinda Murray Ratini DO
Date Last Reviewed:
1/1/2025
© 2000-2026 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.